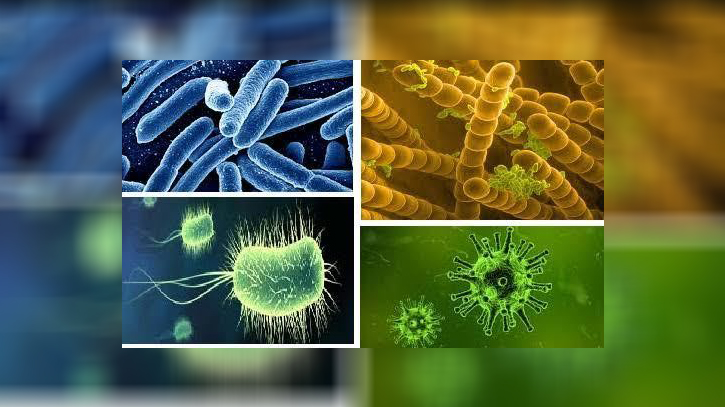
A note on microorganisms
Shopnil Akash || risingbd.com

They are very small particles! We cannot see them with our naked eye. Although seemingly insignificant, we feel their presence in our daily life at every moment! Yoghurt is made from milk, wine from fruits, cakes and biscuits from flour. On the other hand, they are also the cause of the most terrible diseases in the world.
Microorganisms are basically divided into four groups: bacteria, viruses, protozoa and fungi. All of them are very small in size: one millionth of a meter or less. Some exceptional protozoa are slightly larger but never larger than 1 millimeter.
Although tiny in size, microorganisms are unimaginably larger in number than humans or any other animal on earth. The number of people in the world today is approximately 7,000,000,000.
Recently, a team of scientists from the University of Georgia sat down to count the total number of bacteria in the world and were stunned. That number is about 5,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 (five trillion.)
Scientists think that the emergence of microorganisms was come to the earth millions of years ago. That is about 3,600,000,000 years ago. The history of human civilization is much younger than that. The history of human in the world is approximately 200,000 years. During this long period of time, microorganisms have always been around people, but no one knew about them before October 9, 1676.
These small microbes were first discovered by a Dutch scientist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. He is therefore called the father of bacteriology. At the time, however, Anthony Phillips van Leeuwenhoek did not know that it was for these microorganisms that yogurt was made from milk, to digest food, or that these insignificant microbes could cause serious diseases such as plague, cholera or tuberculosis.
About two hundred years later, French scientists Louis Pasteur and German scientist Robert Koch first identified germs as the cause of various human diseases. Robert Cock proves that cholera and tuberculosis disease caused by two separate microbes.
He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1905 for his outstanding contributions to bacteriology. Robert Cock's contemporaries were Louis Pasteur and Ferdinand Julius Cohn. Louis Pasteur was the first to give the idea about the vaccine to cure a bacterial disease.
He invented the method of pasteurization of liquid drinks (milk, wine, etc.). Even today, that method is used to preserve liquid, milk in daily life. Another contemporary discovery in bacteriology is the discovery of the antibiotic penicillin. The Scottish scientist Alexander Fleming has discovered penicillin antibiotics in 1929. The discovery of antibiotics is considered a significant milestone in the history of bacteriology.
Although we have often heard of the name of, Louis Pasteur, Ferdinand Koh'n, Robert Cock or Alexander Fleming in many places, The Dutch scientist Martinus Beijerinck largely ignored.By discovering the virus, he added a new dimension to microbiology.
Prior to his discovery, germs meant only bacteria. In 1896, he proved that the cause of the infectious disease of tobacco was a tiny germ, but its size was several times smaller than that of bacteria. He named the newly discovered virus (Tobacco Mosaic Virus: TMV).
At the time, his idea was that the virus was much like a jelly or liquid organism. However, it was virtually impossible to detect viruses under a microscope at that time.
Later, with the discovery of the electron microscope by German scientist Max Knoll and Ernst Ruska in 1931, it became possible to learn much more about the structure of the virus. Various experiments with X-ray crystallography and electron microscopy first showed in 1941 that viruses were actually particles with a specific structure.
Various studies on viral science or virology estimate that there are approximately one million types of viruses in the world. As I said before, the number of bacteria in the world is approximately 5 x 1030, and the total number of viruses is almost double that!
Now you can think if the microorganisms are just small particles, so, why can’t we find a way to protect ourselves from these tiny microorganisms even in today's age of scientific advancement?
Yet the number of people infected with Vibrio cholera each year is 30-40 million, the number of people infected with tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) is 60-70 million (deaths over one million) and the number of people infected with Tetanus (Clostridium tetani) is 5-12 million ( Death more than fifty thousand). Not only this, with the help of pneumonia, diphtheria, meningitis, gonorrhea, bronchitis, tuberculosis, typhoid, plague and many more deadly diseases is caused by microorganisms. More research can be conducted to know more about these tiny microorganisms.
Shopnil Akash is currently studying Pharmacy at the Daffodil International University
DIU/Mahfuz/AI