Climate change in Bangladesh: Reality, impacts and solutions
SM Mostafijur Rahman || risingbd.com
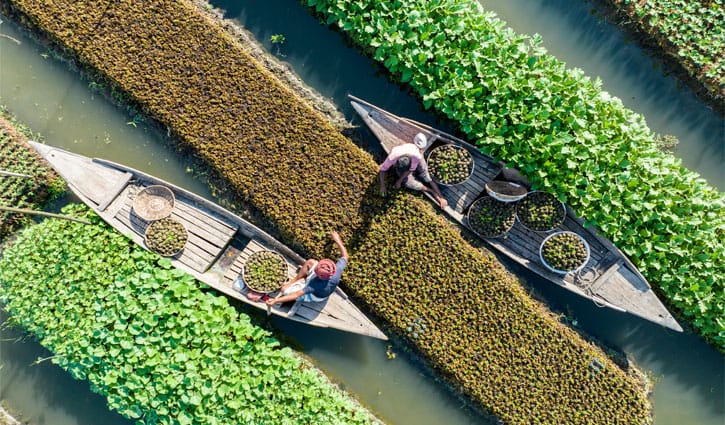

Floating farming to maintain crop production in low-lying areas that are submerged or affected by climate change
Climate change is currently a globally discussed and concerning issue. However, its severe impacts are being felt by developing and geopolitically vulnerable countries like Bangladesh. Due to its geographical location, dense population, poverty, weak infrastructure and river-dependent lifestyle, Bangladesh is one of the main victims of the climate change.
Although Bangladesh's contribution to global greenhouse gas emissions (emission of various gases including carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide in the Earth's atmosphere) is very small, but crore of people in the country are still suffering from its consequences.
The Reality of Climate Change in Bangladesh
Bangladesh is a country located on the banks of the world's largest river systems (Ganga, Brahmaputra and Meghna). In addition, the coastal area of the Bay of Bengal, low-lying terrain and dense population increase Bangladesh's climate sensitivity.
In the past few decades, the country's average temperature has increased, the monsoon pattern has changed, and the number and intensity of cyclones have increased. On the one hand, crop production in the northern region is being disrupted due to drought. On the other hand, the land on the coast is becoming unsuitable for cultivation due to salinity and tidal surges.
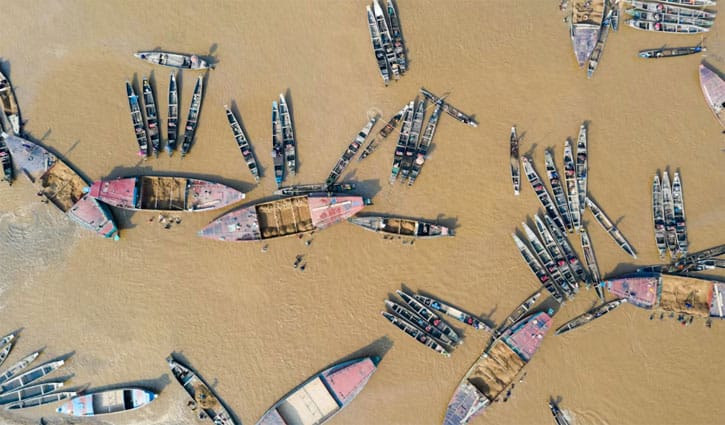

Locals are busy extracting stones and coal from the river along with the floodwaters coming down from upstream.
Impacts of climate change in Bangladesh
1. Coastal regions under threat
The southern region of Bangladesh, including coastal districts such as Khulna, Bagerhat, Satkhira, Patuakhali, Bhola, etc., are direct victims of climate change. Salinity has increased greatly in these areas due to rising sea levels and frequent cyclones. Agricultural production is declining due to declining soil fertility. Many families are being forcibly displaced, which is a new crisis: "climate refugees".
2. Cultivation and food security
The seasonal normality of agriculture is being destroyed due to the impact of climate change. The rain that used to be at specific times is now sometimes excessive, sometimes absent altogether. This is having a negative impact on the production of many agricultural products including rice, jute, wheat, and potatoes. As a result, food security is under threat, which can increase poverty and malnutrition.
3. Increased health risks
Due to high temperatures, water scarcity, and pollution, the incidence of diseases such as diarrhea, dengue, malaria, and heatstroke is increasing in Bangladesh. Heatstroke is continuously increasing in urban areas, which is affecting children and the elderly more.
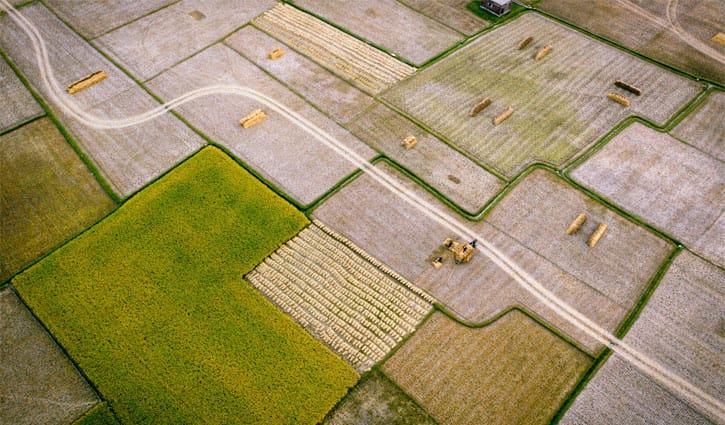

Farmers are harvesting rice, the main food grain of Bangladesh.
4. Increased intensity of natural disasters
Storms such as cyclones 'Sidr' (2007), 'Aila' (2009), 'Amphan' (2020) etc. prove that natural disasters are now becoming more destructive in Bangladesh. In addition to the loss of life in such disasters, education, health, transportation, and agricultural systems are also severely affected.
5. Impact on dietary habits and livestock
Climate change has had a huge impact on dietary habits and livestock. Rising temperatures, changes in rainfall, and natural disasters have led to a food crisis for livestock. As a result, the health, reproductive capacity, and milk production of livestock have also decreased. At the same time, diseases, pests, and parasitic infections are also increasing due to climate change, which has made the lives of livestock more difficult.
Bangladesh government’s initiatives to combat climate change
The Bangladesh government has taken several initiatives to combat climate change. These include the formation of a climate change trust fund, the formulation of a climate change strategy and action plan, and increasing the use of renewable energy. In addition, the government is also working to combat this crisis by adopting adaptation projects in coastal areas, developing disaster management, and increasing international cooperation. In 2009, the ‘Bangladesh Climate Change Strategy and Action Plan (BCCSAP)’ was prepared. Various projects have been taken under it, such as: rebuilding and developing coastal embankments, establishing and expanding cyclone shelters, developing salinity-tolerant rice varieties, and environmentally friendly solar-powered irrigation systems.
Bangladesh is the first country in the world to achieve climate-resilient development by 2041 through the ‘Climate Prosperity Plan’, which has been chairing the “Climate Vulnerable Forum” (CVF) and demanding global climate justice.
Things to do to combat climate change
1. Expanding the use of renewable energy
Reducing dependence on fossil fuels by increasing the use of solar energy, wind energy, biogas, etc. This will reduce environmental pollution and will lead to self-reliance in the energy sector in the long term.
2. Afforestation and environmental conservation
The amount of forests should be increased. Rivers, canals, beels and water bodies should be preserved. Cutting down mountains should be stopped and policies should be formulated to increase green areas in cities.
3. Increasing public awareness
Environmental education should be made mandatory in schools and colleges. People should be made aware through the media, social media, religious and social organizations.
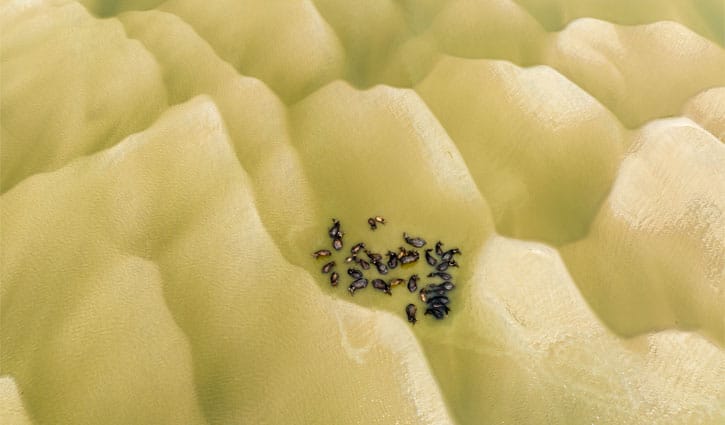

A herd of buffaloes are resting in the Padma River to escape the intense heat.
4. Spreading climate adaptation technologies
Innovation of salt-tolerant and drought-resistant crops, construction of flood-resistant houses, and introduction of modern water conservation systems should be implemented.
5. Demand for international support and justice
Climate funds should be ensured for the needs of countries like Bangladesh. Developed countries should accept responsibility for environmental pollution and increase financial and technological support.
Climate change is not just an environmental crisis, it is also a humanitarian, economic and political crisis. In a climate-sensitive country like Bangladesh, it is extremely important to take immediate and long-term steps to address this crisis. It is possible to pave the way for a sustainable future by not destroying natural resources in the name of development, by adopting environmentally friendly policies and by demanding climate justice internationally.
In addition, several promising efforts are being observed in some regions of the country at the marginal level to prevent the effects of climate change. Among these, floating farming is notable one. Each of us has a responsibility to protect the environment from our own position and spread climate awareness. Because this world is not only ours, but also our next generation.
Dhaka/Mukul